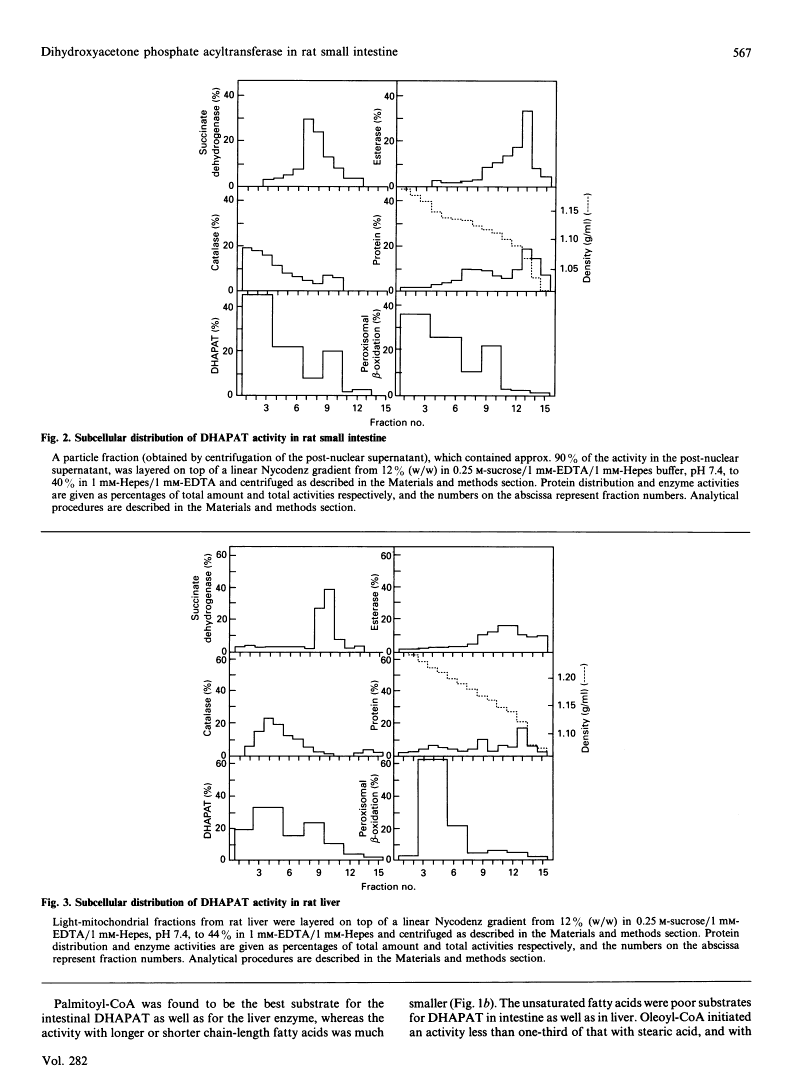
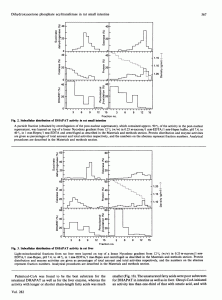
The subcellular localization of dihydroxyacetone phosphate acyltransferase (DHAPAT) exercise in rat small gut was investigated by Nycodenz-gradient centrifugation. We discovered that DHAPAT had a predominant peroxisomal distribution, with a separate enzyme exercise positioned in the microsomal fraction, the identical distribution as discovered in rat liver.
The effect of feeding rats on a weight loss plan with 20% (w/w) partially hydrogenated fish oil (PHFO) or 0.3% clofibrate on the exercise of DHAPAT in rat small gut and liver was studied. Both 20% PHFO and 0.3% clofibrate gave a 1.8-fold stimulation of the precise actions of DHAPAT in peroxisomes of the small gut, whereas in the liver 20% PHFO gave a 1.4-fold stimulation and 0.3% clofibrate a 1.6-fold stimulation of the entire DHAPAT actions in the postnuclear supernatant. The particular actions of DHAPAT in liver weren’t affected.
Conformation of DNA packaged in bacteriophage T7. Analysis by use of ultraviolet light-induced DNA-capsid cross-linking.
The conformation of the linear, double-stranded, 39,936 kilobase-pair DNA packaged in the protein capsid of bacteriophage T7 is investigated right here by use of brief wavelength ultraviolet light-induced DNA-capsid cross-linking.
To detect each DNA-capsid and DNA-DNA cross-links, DNA is expelled from the T7 capsid and the merchandise of expulsion are analyzed by use of Nycodenz buoyant density centrifugation, adopted by both pulsed discipline gel electrophoresis or invariant discipline gel electrophoresis. Short wavelength ultraviolet mild is discovered to progressively induce each DNA-DNA and DNA-protein cross-links in intact bacteriophage T7, however not in T7 from which DNA had been expelled earlier than publicity to ultraviolet mild. Protein-protein cross-links should not induced.
When DNA expelled from beforehand cross-linked T7 is cleaved with restriction endonuclease (1 to three websites cleaved), evaluation of the ensuing fragments reveals no areas on T7 DNA which might be excluded from cross-linking to the capsid.
However, the effectivity of cross-linking decreases as the gap from the left finish (final finish packaged) of the packaged DNA will increase. Electron microscopy of negatively stained capsid-DNA complexes reveals no DNA-retaining construction aside from the outer shell of the capsid.
Together with beforehand reported knowledge that point out lack of protein-based specificity for ultraviolet light-induced cross-linking, these observations are interpreted by the assumptions that, inside the limits of decision of these experiments: (1) no area of packaged T7 DNA is excluded from contact with the outer shell of the T7 capsid; (2) the chance of contacting the outer shell decreases as the gap from the left finish of packaged T7 DNA will increase. Thus, T7 DNA packaging concentrates the final finish packaged close to the inside floor of the outer shell of the T7 capsid.